Dynamic MCP
Route to a Model Context Protocol (MCP) server dynamically by using a label selector. This way, unlike a static backend, you can update the backing MCP server without having to update the Backend resource. For more information, see the About MCP topic.
Before you begin
Set up an agentgateway proxy.
Step 1: Deploy an MCP server
Deploy an MCP server that you want agentgateway to proxy traffic to. The following example sets up an MCP server that provides various utility tools.
-
Create an MCP server (
mcp-server) that provides various utility tools. Notice the following details about the Service:appProtocol: kgateway.dev/mcp(required): Configure your service to use the MCP protocol. This way, the agentgateway proxy uses the MCP protocol when connecting to the service.kgateway.dev/mcp-pathannotation (optional): The default values are/ssefor the SSE protocol or/mcpfor the Streamable HTTP protocol. If you need to change the path of the MCP target endpoint, set this annotation on the Service.
kubectl apply -f- <<EOF apiVersion: apps/v1 kind: Deployment metadata: name: mcp-server-everything labels: app: mcp-server-everything spec: replicas: 1 selector: matchLabels: app: mcp-server-everything template: metadata: labels: app: mcp-server-everything spec: containers: - name: mcp-server-everything image: node:20-alpine command: ["npx"] args: ["-y", "@modelcontextprotocol/server-everything", "streamableHttp"] ports: - containerPort: 3001 --- apiVersion: v1 kind: Service metadata: name: mcp-server-everything labels: app: mcp-server-everything spec: selector: app: mcp-server-everything ports: - protocol: TCP port: 3001 targetPort: 3001 appProtocol: kgateway.dev/mcp type: ClusterIP EOF -
Create a Backend for your MCP server that uses label selectors to select the MCP server.
kubectl apply -f- <<EOF apiVersion: gateway.kgateway.dev/v1alpha1 kind: Backend metadata: name: mcp-backend spec: mcp: targets: - name: mcp-server-everything selector: services: matchLabels: app: mcp-server-everything EOFℹ️Plan to attach policies to your selector-based Backend later? You can still attach the policy to a particular backing Service. To do so, set thetargetRefsetting in the policy to the backing Service, not to the Backend’s service selector. Include thesectionNameof the port that you want the policy to apply to. For an example, check out the BackendTLSPolicy guide.
Step 2: Route with agentgateway
Create an HTTPRoute resource that routes to the Backend that you created in the previous step.
kubectl apply -f- <<EOF
apiVersion: gateway.networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: HTTPRoute
metadata:
name: mcp
labels:
example: mcp-route
spec:
parentRefs:
- name: agentgateway-proxy
namespace: kgateway-system
rules:
- backendRefs:
- name: mcp-backend
group: gateway.kgateway.dev
kind: Backend
EOFStep 3: Verify the connection
Use the MCP Inspector tool to verify that you can connect to your MCP server through agentgateway.
-
Get the agentgateway address.
export INGRESS_GW_ADDRESS=$(kubectl get gateway agentgateway-proxy -n kgateway-system -o=jsonpath="{.status.addresses[0].value}") echo $INGRESS_GW_ADDRESSkubectl port-forward deployment/agentgateway-proxy -n kgateway-system 8080:80 -
From the terminal, install the MCP Inspector tool. Then, the MCP Inspector opens in your browser. If the MCP inspector tool does not open automatically, run
mcp-inspector.npx modelcontextprotocol/inspector#0.18.0 -
From the MCP Inspector menu, connect to your agentgateway address as follows:
- Transport Type: Select
Streamable HTTP. - URL: Enter the agentgateway address, port, and the
/mcppath. If your agentgateway proxy is exposed with a LoadBalancer server, usehttp://<lb-address>/mcp. In local test setups where you port-forwarded the agentgateway proxy on your local machine, usehttp://localhost:8080/mcp. - Click Connect.
- Transport Type: Select
-
From the menu bar, click the Tools tab, then click List Tools.
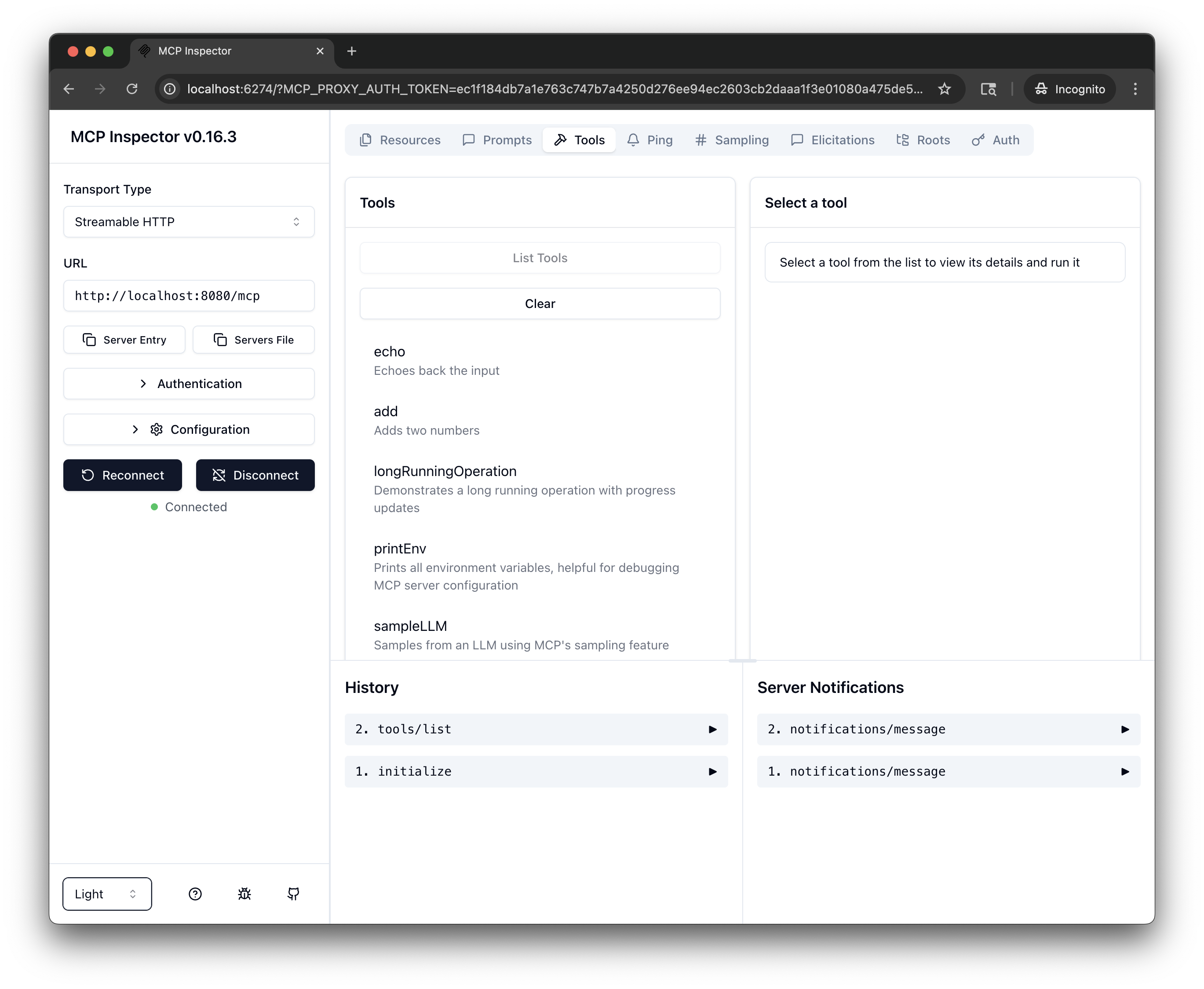
-
Test the tools: Select a tool, such as
echo. In the message field, enter a message, such asHello, world!, and click Run Tool.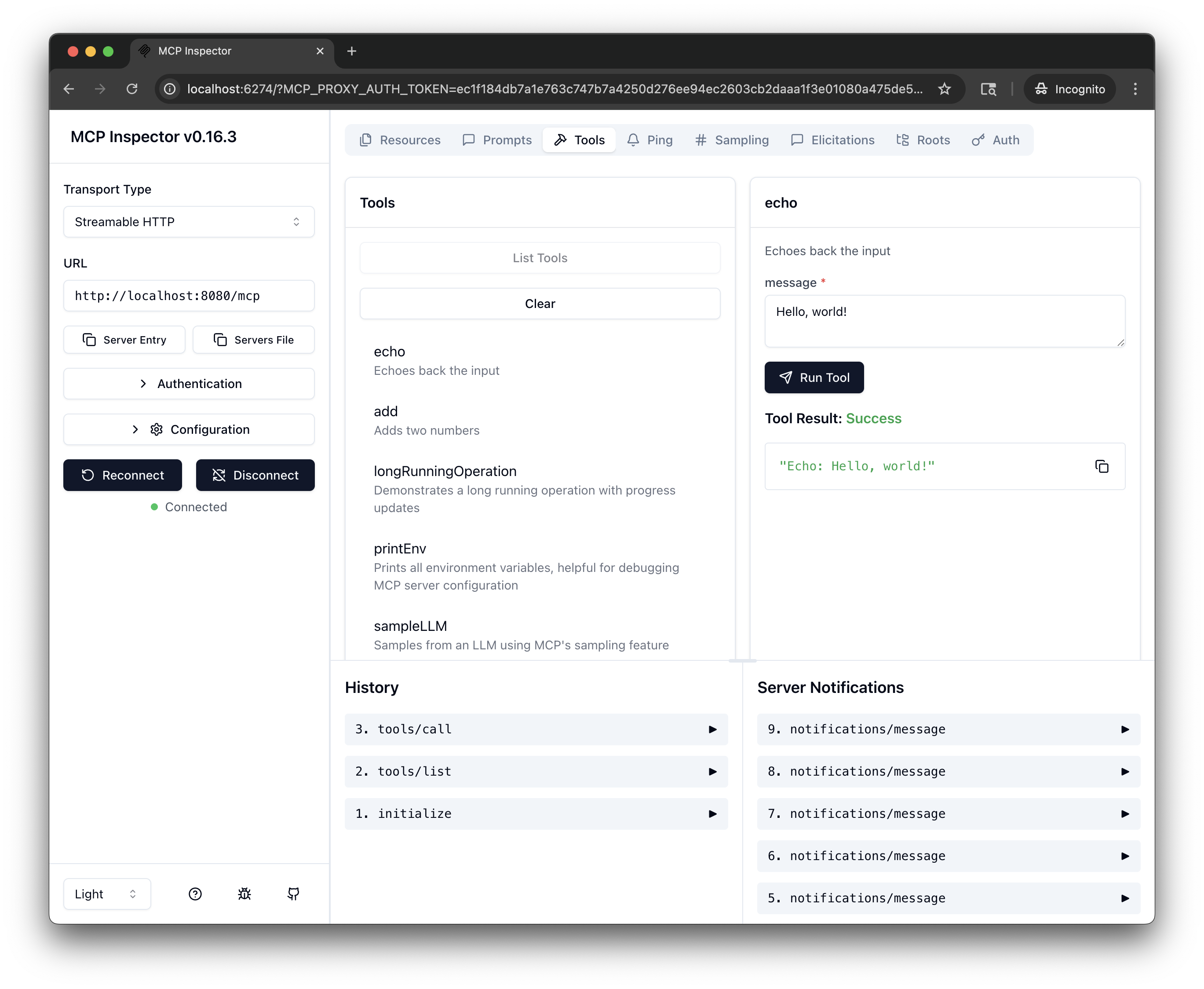
Cleanup
You can remove the resources that you created in this guide.kubectl delete Deployment mcp-server-everything
kubectl delete Service mcp-server-everything
kubectl delete Backend mcp-backend
kubectl delete HTTPRoute mcp